
Below is a comprehensive, beginner-friendly, yet deeply detailed guide to Boolean Algebra, complete with definitions, laws, proofs, truth tables, real-world applications, and examples to help you on your software development journey.


1. What Is Boolean Algebra?
Boolean Algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with binary values — values that can only be:
- 1 or 0
- True or False
- High or Low
It was introduced by George Boole, a mathematician and logician, to describe the rules of logical reasoning.
Today, Boolean algebra is the foundation of:
- Digital electronics
- Computer architecture
- Programming logic
- Search algorithms
- Switching circuits
It is the mathematics of logic operations.
2. Boolean Variables
In Boolean algebra, variables can hold only two possible values:
| BOOLEAN VALUE | MEANING |
|---|---|
| 1 | True / ON / High |
| 0 | False / OFF / Low |
Example Boolean variables:
A = 1
B = 0
3. Basic Boolean Operators
Boolean algebra works with three fundamental operators:


1. AND ( · )
- Written as A·B or AB
- Output is 1 only when both inputs are 1
| A | B | A·B |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
2. OR ( + )
- Output is 1 when any input is 1
| A | B | A + B |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
3. NOT ( ¬ or ̅ )
- Inverts the input
- If A = 1 → A̅ = 0
| A | NOT A |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
4. Derived Boolean Operators
NAND
- NOT AND
- A NAND B = (AB)̅
NOR
- NOT OR
- A NOR B = (A + B)̅
XOR (Exclusive OR)
- Output is 1 when inputs are different
| A | B | A ⊕ B |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
5. Boolean Algebra Laws
A. Identity Laws
- A + 0 = A
- A · 1 = A
B. Null Laws
- A + 1 = 1
- A · 0 = 0
C. Idempotent Laws
- A + A = A
- A · A = A
D. Complement Laws
- A + A̅ = 1
- A · A̅ = 0
E. Commutative Laws
- A + B = B + A
- A · B = B · A
F. Associative Laws
- (A + B) + C = A + (B + C)
- (AB)C = A(BC)
G. Distributive Laws
- A(B + C) = AB + AC
- A + BC = (A+B)(A+C)
H. Absorption Laws
- A + AB = A
- A(A + B) = A
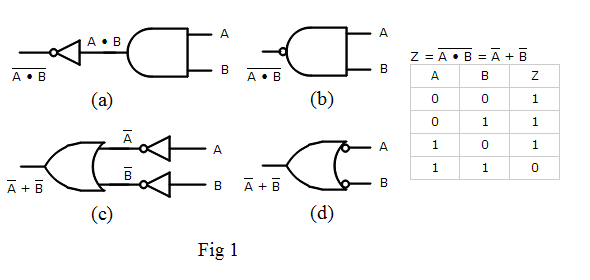
I. De Morgan’s Laws
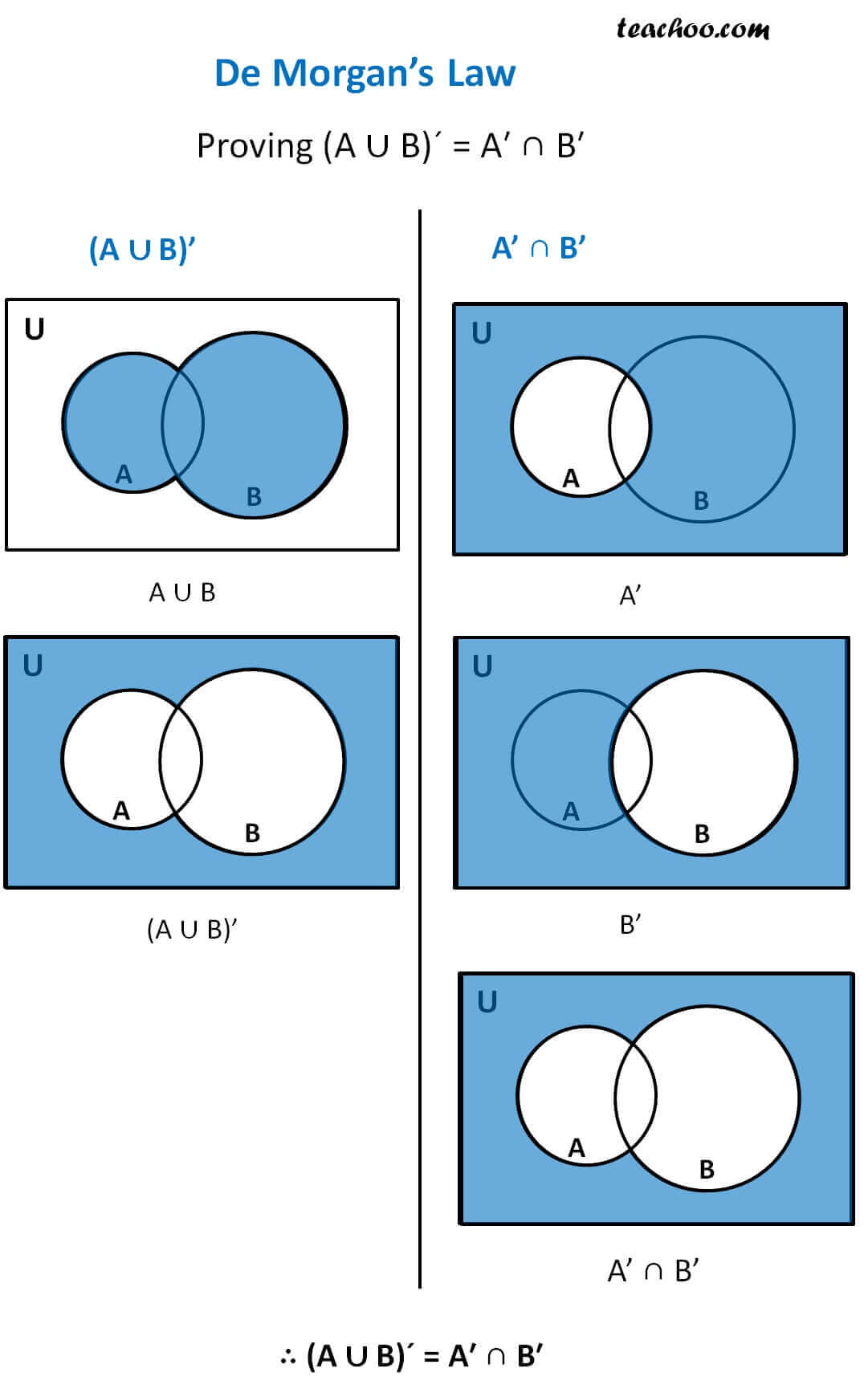

- (A·B)̅ = A̅ + B̅
- (A + B)̅ = A̅ · B̅
These laws are extremely important in circuit design.
6. Simplifying Boolean Expressions
Example 1
Simplify:
A + AB
Using Absorption Law:
A + AB = A(1 + B)
1 + B = 1
So:
A + AB = A
Example 2
Simplify:
AB + A̅B
Factor out B:
= B(A + A̅)
But A + A̅ = 1
Therefore:
AB + A̅B = B
Example 3
Simplify using De Morgan:
(A + B)̅
= A̅ · B̅
7. Boolean Algebra & Logic Circuits
Boolean expressions correspond directly to logic circuits.



| Boolean Expression | Logic Gate Equivalent |
|---|---|
| A + B | OR gate |
| AB | AND gate |
| A̅ | NOT gate |
| (A + B)̅ | NOR gate |
| (AB)̅ | NAND gate |
8. Karnaugh Maps (K-Maps) — For Simplification
K-maps are grid techniques for reducing Boolean expressions.
Useful for:
- 2-variable
- 3-variable
- 4-variable
Example 2-variable K-map:
| AB | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | ||
| 1 |
K-maps group 1s to minimize expressions.
9. Applications of Boolean Algebra
1. Digital Electronics
Used to design:
- Microprocessors (e.g., Intel Core i7)
- Memory units (e.g., Samsung DDR5 RAM)
- Logic circuits
2. Programming
Boolean conditions drive:
- if statements
- loops
- conditional rendering
Used in languages such as:
- Python
- JavaScript
- Java
3. Search Engines
Google uses Boolean operators like:
- AND
- OR
- NOT
4. Databases
SQL WHERE clauses use Boolean expressions.
5. Cybersecurity
Firewalls use Boolean logic to allow/deny rules.
6. Control Systems
Sensors work with True/False signals.
10. Full Example With Truth Table and Circuit
Simplify and implement:
Expression:
F = AB + A̅C
Truth Table
| A | B | C | AB | A̅C | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
Logic Circuit
- AND gate for AB
- NOT A, AND with C
- OR gate to combine
11. Why Boolean Algebra Matters
Boolean algebra is the language of computers.
Everything from your phone CPU to apps like
Facebook
and
Instagram
depends on Boolean logic for decision-making.
Without Boolean algebra, modern computing would not exist.

Latest tech news and coding tips.



